Bore water (Groundwater)
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water sourced from below the earth’s surface. Excess water in the soil seeps through the ground until it reaches a level where the spaces within sediments or rocks are saturated with water. This is called the water table. Water in the saturated zone below the water table is called groundwater.
Groundwater moves very slowly, compared to rivers and streams, because it has to flow through small openings in layers of soil, sediment and rock. A rock or sediment layer that is capable of yielding useful supplies of groundwater is called an aquifer. Groundwater from aquifers can be brought to the surface by constructing bores or wells and installing a pump.
Bore water or groundwater is an extremely important resource across Australia. More information on groundwater in NSW including the management and allocation of groundwater is available on the NSW Department of Planning, Industry and Environment website.
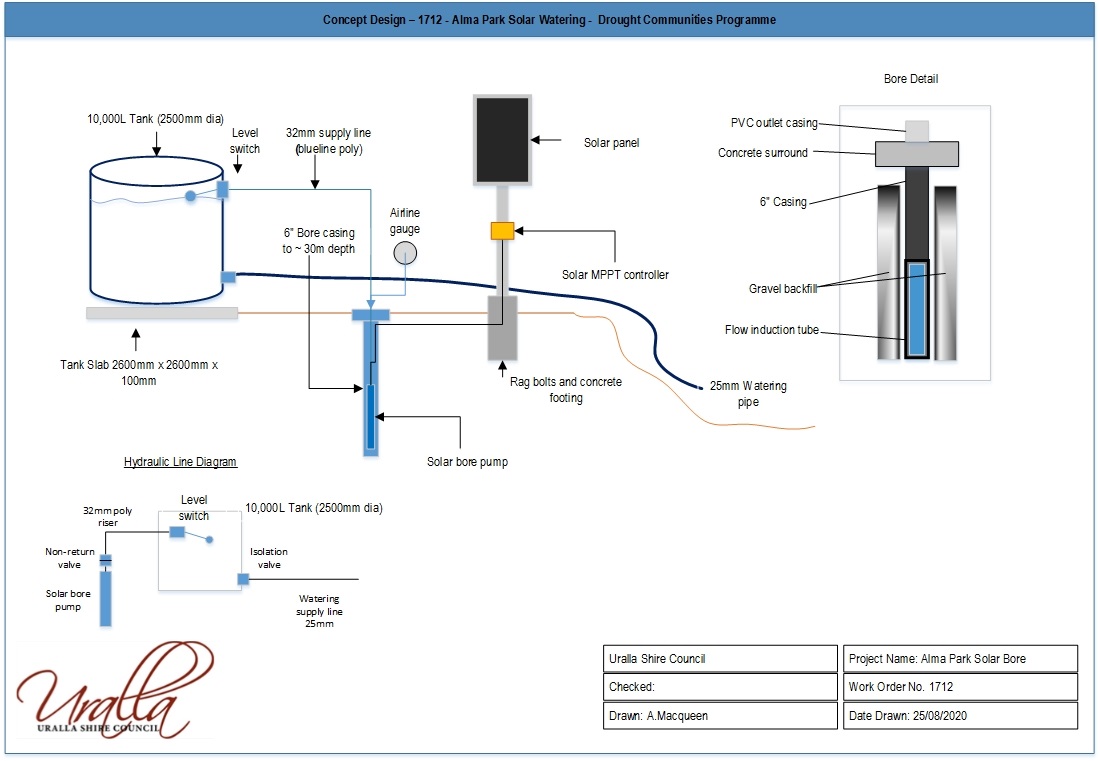
Alma Park Bores
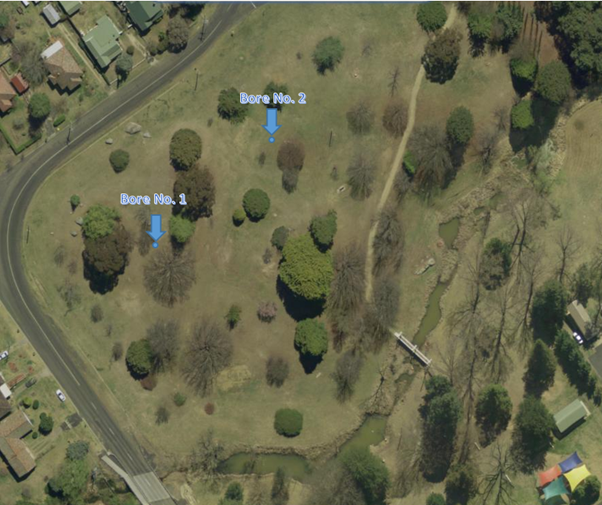
Two bores have been installed in Alma Park, Uralla funded by the Australian Government’s Drought Communities Program Extension 2019.
Council obtained a water licence from the Department of Planning, Industry & Environment in 2020 to construct the bores.
The construction of the bores was completed in December 2020.
The project’s objective is to deliver Council’s commitment to the community to secure sustainable and environmentally sound water-cycle infrastructure and services.
The primary purpose of the Alma Park bores is to extract water during periods of prolonged drought to preserve heritage trees on community land.
Bore Data
Bore No. 1
|
Depth (m)
|
Daily Yield (L)
|
Water quality
|
Bore use
|
Comments
|
|
54 m
|
1800 L
|
Unknown (sampling not allowed until NRAR licence issued.)
|
Drought affected trees of cultural significance.
|
Ground penetrating studies in this area do not indicate significant volumes of water.
|
Bore No. 2
|
Depth (m)
|
Daily Yield (L)
|
Water quality
|
Bore use
|
Comments
|
|
36 m
|
1400 L
|
Unknown (sampling not allowed until NRAR licence issued.)
|
Drought affected trees of cultural significance.
|
Ground penetrating studies in this area do not indicate significant volumes of water.
|

Bore water as a water supply source
NSW Health recommends that groundwater is not used for drinking, cooking and personal hygiene (including cleaning teeth and bathing) without testing and appropriate treatment including disinfection.
Potable water that is treated to remove pathogens should always be the first choice for your drinking water. Untreated bore water can be used for irrigation, livestock watering, garden watering, and for domestic uses such as flushing toilets and clothes washing.
NSW Health recommends that users of groundwater be familiar with the quality of their water. This can be done by testing the microbiological, chemical and radiological quality of the water. Water used for household purposes such as drinking, food preparation and personal hygiene (including cleaning teeth/oral hygiene and bathing) should meet water quality guidelines in order to protect you and your family’s health.
For more information, visit NSW Health’s Groundwater page.